You spin my head right round… 😵💫
Seeing a spinner after every click isn’t fun. We began seeing this at Chronicle a while after our private beta launch. Every time you switched documents from the sidebar, it would take upwards of 4-5 seconds to get into editing. It sucked big time.
Initial investigation led us to identifying Yjs, which we used as our primary document store, was sending a massive initial websocket message (>2MB) via websockets when we connected to the server.
Culprit ⁉️
Why was the document (Y.Doc) so large?
Our initial hunch was our extensive use of Y.Maps, which does not make use of Yjs’ optimizations if key value writes are in an alternating order.
I created a synthetic benchmark where I simulated repeated random writes that we do (movement/content changes/etc) to a Y.Doc with a Y.Map. The results were pretty terrible (8MB lol damn) and it confirmed our suspicions.
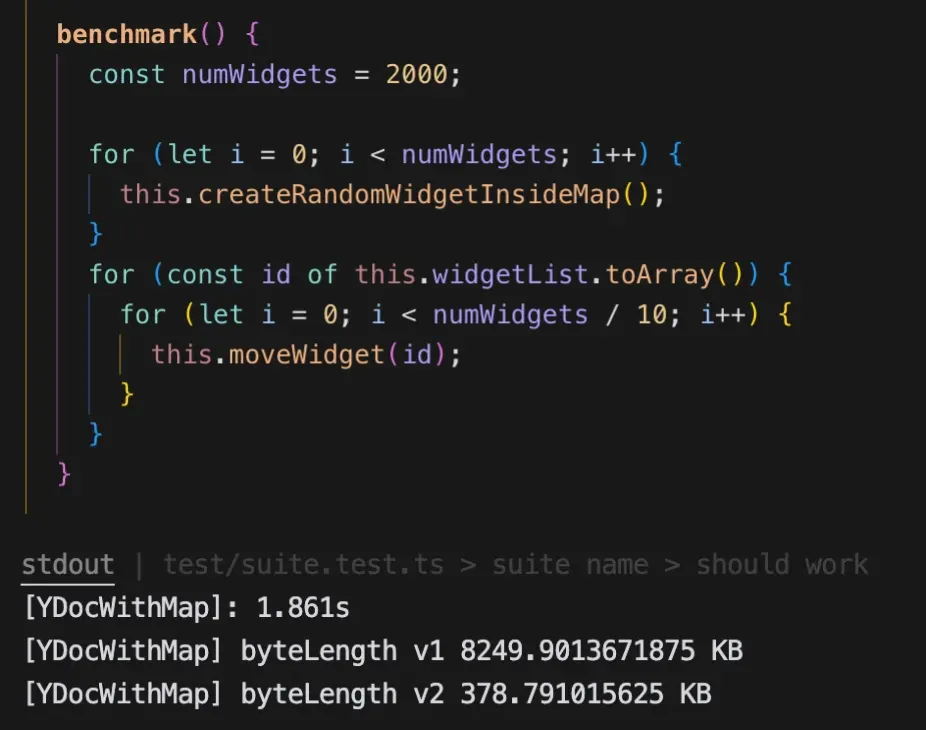
Now we have identified the culprit - but what could we do to fix it?
Some Yjs jargon
Although we do not go into depth about Yjs here, only its surrounding ecosystem and sync protocols - some of the terms and phrases will likely not make sense. Here’s a small primer:
-
Yjs: A Conflict-free Replicated Data Types (CRDTs) implementation. CRDTs are special data structures that can be modified concurrently by multiple users, and when the changes are combined together, they will always merge together in a consistent state.
-
y-protocols: Synchronization and encoding protocols used by Yjs. It defines how different peers communicate with each other to exchange and apply document updates. What we will look at is the message formats and the exchange of
SyncStep1andSyncStep2messages during document synchronization. -
Yjs providers: A “provider” is what connects a Yjs document to other clients (through a network) or that synchronizes a document with a database.
y-websocketis one such provider, and Liveblocks gives us their Yjs provider,LiveblocksYjsProviderto sync with their storage. -
y-websocket: This is one implementation of
y-protocols. It uses WebSockets as the transport layer for sending synchronization messages between multiple clients. -
Y.Doc: Represents a shared document, tracks all changes, and manages the state of shared types (like
Y.Array,Y.Map,Y.Text). Each user who collaborates on the same document will have their ownY.Docinstance. -
State Vector: Compact representation of the state of a local document. It’s essentially a map of
clientIds toclockvalues, which is used to generate efficient updates when syncing clients. -
Updates: Changes on the shared document are encoded into binary encoded (highly compressed) document updates. Document updates are commutative, associative, and idempotent. This means that you can apply them in any order and multiple times. All clients will sync up when they receive all document updates.
-
encodeStateAsUpdate: This method encodes the document state as a single update message that can be applied on other documents (aka other clients). Optionally, specifying the target state vector returns only the missing differences to the update message.
-
applyUpdate: Once a peer receives an update (for example via
SyncStep2), this is the method used to apply a document update on the shared document. -
clientID and clock: Every operation in Yjs has a unique identifier
ID(clientId, clock), where theclientIdrepresents the client that made the change, and theclockis an ever increasing counter for that specific client.
Potential solutions to our problem
One promising avenue was Yjs’ encodeStateAsUpdateV2 method for creating the initial state vector. This was a confirmed way of reducing the document size (evident from the benchmark) as it compresses larger documents much better than the v1 implementation, trading off the efficiency in smaller Y.Docs.
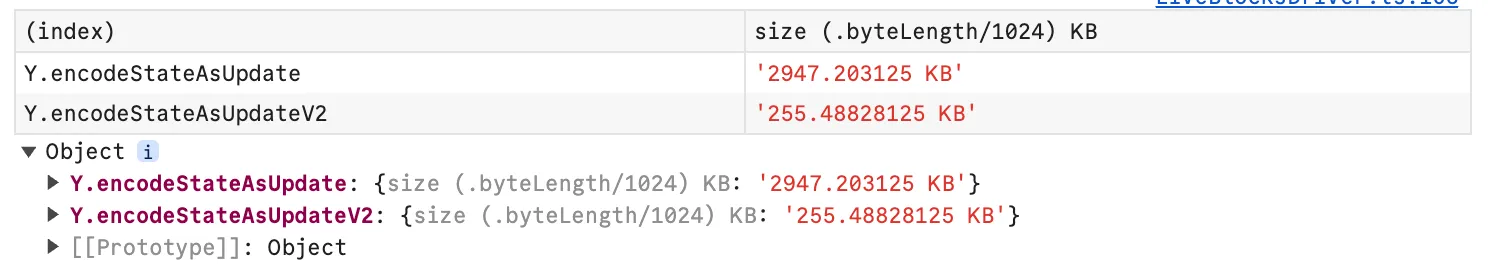
Unfortunately, our chosen Yjs provider, Liveblocks, didn’t support this method at the time. It was also not mentioned in the Yjs docs, meaning it could very well be experimental. After some back-and-forth with the fantastic people at Liveblocks, it became apparent that we needed to look for alternative strategies.
To properly come up with other useful strategies, we need to understand Yjs’ sync behavior, and why the initial payload can grow so large.
Yjs sync flow - y-protocols
The Yjs synchronization process relies on the standards and implementation defined by the y-protocols library. It has the following major steps:
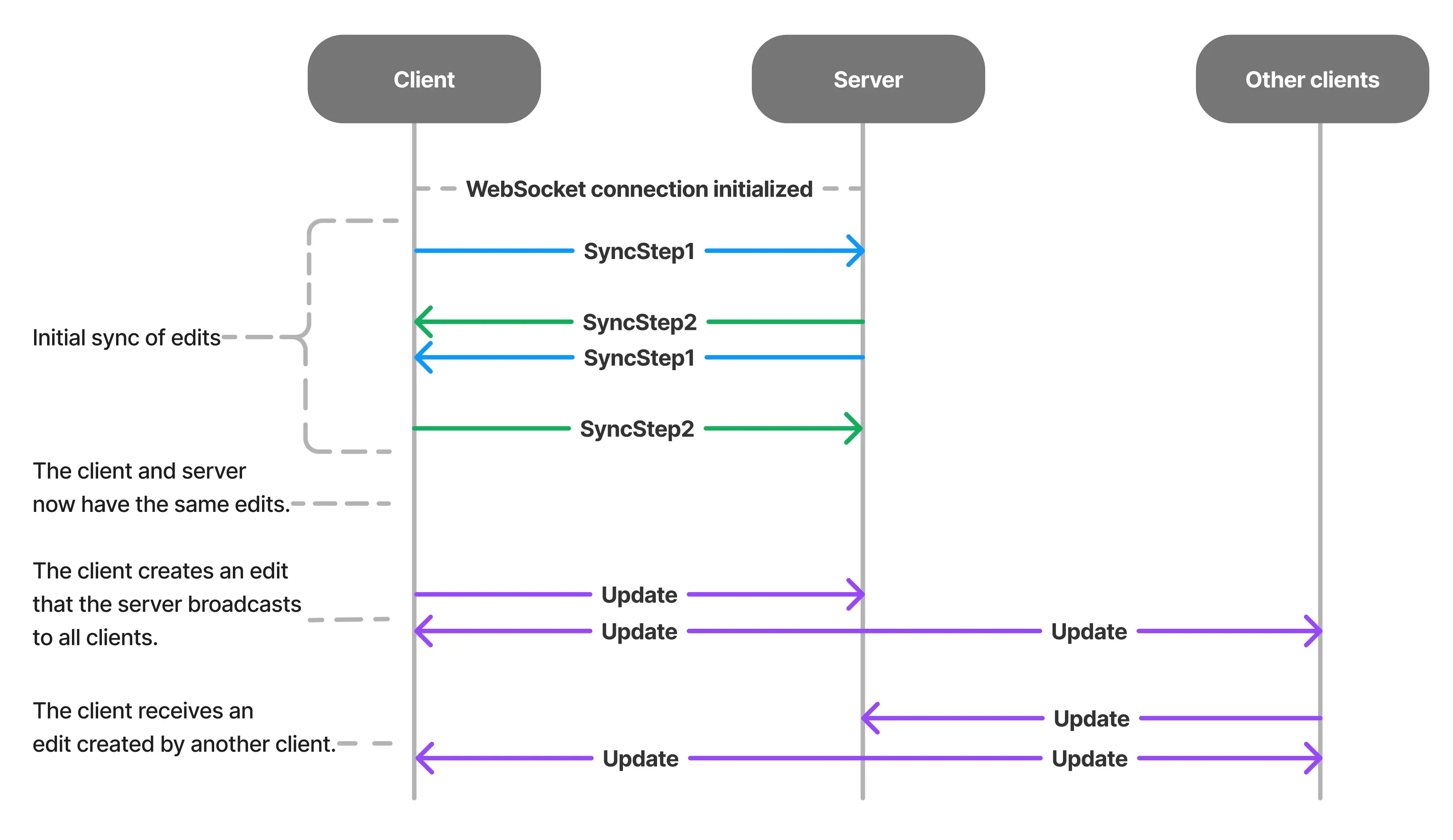
0. WebSocket connection initiate ↔
This is the setup phase where a WebSocket connection between the client and server is established.
1. Client initiates sync with SyncStep1 request ↗
// y-protocols/sync.js
//
export const messageYjsSyncStep1 = 0;
// ...
export const writeSyncStep1 = (encoder, doc) => {
encoding.writeVarUint(encoder, messageYjsSyncStep1);
// on the client which initiated connection
// encode the current state of the doc and send it to server
const sv = Y.encodeStateVector(doc);
encoding.writeVarUint8Array(encoder, sv);
};writeSyncStep1(encoder, doc): This function is called by the client to initiate the sync.Y.encodeStateVector(doc): This creates a state vector from the currentY.Docinstance, mappingclientIdto theirclock.- The state vector is then written to the
encoderand sent to the server.
The client is telling the server, “Here’s what I know about the document till this point in time. Send me only what’s missing”
2. SyncStep1 processed by server, SyncStep2 response ↙
// y-protocols/sync.js
export const messageYjsSyncStep2 = 1;
/**
* Read SyncStep1 message and reply with SyncStep2.
*
* @param {decoding.Decoder} decoder The reply to the received message
* @param {encoding.Encoder} encoder The received message
* @param {Y.Doc} doc
*/
export const readSyncStep1 = (decoder, encoder, doc) =>
writeSyncStep2(encoder, doc, decoding.readVarUint8Array(decoder));
// ...
/**
* @param {encoding.Encoder} encoder
* @param {Y.Doc} doc
* @param {Uint8Array} [encodedStateVector]
*/
export const writeSyncStep2 = (encoder, doc, encodedStateVector) => {
encoding.writeVarUint(encoder, messageYjsSyncStep2);
// State vector received from request + remote doc on server
// used to compute all document updates missing on the client
const update = Y.encodeStateAsUpdate(doc, encodedStateVector);
encoding.writeVarUint8Array(encoder, update);
};-
readSyncStep1(decoder, encoder, doc): This function is called on the server when aSyncStep1message is received. It reads the state vector sent by the client. -
writeSyncStep2(encoder, doc, encodedStateVector): This function prepares theSyncStep2response, callingY.encodeStateAsUpdate(doc, encodedStateVector). -
Y.encodeStateAsUpdate(doc, encodedStateVector): This is where the server’sY.Docuses the client’s state vector to compute the difference between the server’s document and the client’s document. It identifies the specific updates that the client is missing, and packages just that into an efficient response state vector.
The response will be sent back to the client, containing the SyncStep2 message, informing the client of updates that it is missing.
In a client-server model (like with y-websocket), the server will also send its own SyncStep1 message immediately after sending the SyncStep2 message (see diagram), to ensure that it’s up-to-date with all operations made by the client.
3. Client processes received SyncStep2 and finishes sync ↻
// y-protocols/sync.js
/**
* Read and apply Structs and then DeleteStore to a y instance.
*
* @param {decoding.Decoder} decoder
* @param {Y.Doc} doc
* @param {any} transactionOrigin
*/
export const readSyncStep2 = (decoder, doc, txOrigin) => {
try {
// Apply all the received document updates
// up-to-date with respect to server
Y.applyUpdate(doc, decoding.readVarUint8Array(decoder), txOrigin);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Caught error while handling a Yjs update", error);
}
};readSyncStep2(decoder, doc, transactionOrigin): This function, called on the client, processes the receivedSyncStep2message.decoding.readVarUint8Array(decoder)is used to extract the update messageY.applyUpdate(doc, update, transactionOrigin): This takes the update message and applies all missing operations on the client’sY.Doc, thus bringing the localY.Docup to date with the server’s state.
The client is now in sync with the server, having received every update that it was missing.
4. Subsequent updates (peer edits)
// y-protocols/sync.js
export const messageYjsUpdate = 2;
/**
* @param {encoding.Encoder} encoder
* @param {Uint8Array} update
*/
export const writeUpdate = (encoder, update) => {
encoding.writeVarUint(encoder, messageYjsUpdate);
encoding.writeVarUint8Array(encoder, update);
};
// y-protocols/sync.js
/**
* Read and apply Structs and then DeleteStore to a y instance.
*
* @param {decoding.Decoder} decoder
* @param {Y.Doc} doc
* @param {any} transactionOrigin
*/
export const readUpdate = readSyncStep2;
// method which handles all types of sync messages
export const readSyncMessage = (decoder, encoder, doc, txOrigin) => {
const messageType = decoding.readVarUint(decoder);
switch (messageType) {
// ...
case messageYjsUpdate:
readUpdate(decoder, doc, txOrigin);
break;
default:
throw new Error("Unknown message type");
}
return messageType;
};When a client makes a local change:
- The client uses
writeUpdate(encoder, update)to send the createdupdateto the server. - The
y-websocketserver receives themessageYjsUpdate, routes the message toreadUpdate, which in turns applies the updates usingY.applyUpdate - The server then broadcasts the new update to every other connected peer, so they can also apply the changes.
The solution™
Going back to our problem with the sync flow in mind, what we need to do is reduce the SyncStep2 message the server sends. To achieve that, we used y-indexeddb to store the updating Y.Doc in IndexedDB, and then the LiveblocksYjsProvider would use that as an initial state to start the sync process.
The flow would look like this:
- On first load, a large state vector would be sent if it is a big document, which would be synced to IndexedDB by the IndexedDB plugin.
- On subsequent loads, we would first populate our
Y.Docfrom IndexedDB, and then start the sync process to y-websocket- This means, that we would have some amount of updates already (when client sends
SyncStep1) - hence, reducing the amount of updates that need to be sent back (SyncStep2) in the response - As Yjs supports composing multiple Yjs providers, we can safely use both
y-websocketandy-indexeddbtogether
- This means, that we would have some amount of updates already (when client sends
- Any peer updates received during a session would also be synced to IndexedDB, thus never needing to receive massive updates (unless you return after a year and your collaborator has worked a lot on the document)
This tremendously reduced our load times and switch times, of course with the trade off that we’d be using some of the users’ browser storage.
It also brought in some inherent complexity regarding managing mismatches in document versions when we underwent a schema upgrade, but we handle that by forcing a full sync when we detect it.
We initially released it under a feature flag in order to limit the blast radius to just us at Chronicle, but now it has been released to all users 🏎️💨
Finishing up
This was a massive needle mover in terms of user experience improvement on Chronicle. The solution was not flashy at all, nor did it need any divine intervention (thankfully 🙏).
A lot of it came down to identifying the bottleneck properly and figuring out how to use existing things to reach a solution which didn’t require rewriting half the codebase or a month of work.
Very satisfying.
References
- Yjs Fundamentals — Part 2: Sync & Awareness by Peter Wooden
- yjs: crdt library by Kevin Jahns
- y-protocols: yjs encoding protocols for syncing
- y-websocket: y-protocols implementation with websockets
- y-indexeddb: sync yjs to browser indexeddb